CONCENTRATION
The concentration of a solution nay be defined as the amount of solute present in the given quantity of the solution. It is used to express the composition of a solution.
The concentration be expressed either qualitatively and quantitatively. For example, qualitatively we can say that a solution may be dilute when the solute is present in lesser amount or it is concentrated when the solute is present in excess.
However it is better to express the concentration quantitatively.
There are several method to express the concentration quantitatively.
1. Mass percentage: Mass percentage of a component in a solution is the mass of the component per 100 g of the solution.
Mass % of a component = 
For example if a solution is described by 10% glucose in water it means that 10 g of glucose is dissolved in 90 g of water.
2. Volume percentage: Volume percentage of a component in a solution is the volume of the component per 100 parts by volume of the solution.
For example 20 % ethanol solution in water means that 20 ml of ethanol is dissolved in 100 ml of solution.
3. Mass by volume percentage: It is the mass of solute dissolved in 100 ml of the solution. This unit is commonly used in medicine and pharmacy.
4. Parts per million: This is the parts of a component per million parts of the solution. It is used when the solute is in traces.
5. Mole fraction: It is the ratio of the number of moles of the component to the total number of the moles in solution (solute +solvent). It is designated by X.
for binary solution (component A and B)
XA + XB = 1
XA = nA/nA+nB similarly XB = nB/nA+nB
6. Molarity: (M) It is the number of moles solutes dissolved in one litre of the solution.
For example 0.5 mol/L (or 0.5 M) solution of sucrose means that 0.50 mol of sucrose has been dissolved in one litre.
7. Molality: (m) It is the number of moles solutes dissolved in one litre of the solution.
8. Normality: (N) It is the number of gram equivalents of solutes dissolved in one litre of the solution. Its unit is gram equivalent per litre.
Normality = Number of gram equivalents of solute / Volume of solution in litres.
Gram equivalents of solute = Mass of solute / Equivalent mass.
For better video explanation of NCERT you can visit to the following link:
For the complete notes on Chapter 2 of NCERT VOLUME 1 of Chemistry Class XII visit the following link :
For any query you can comment on it. Don't forget to like and share.



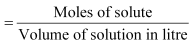

Comments
Post a Comment
If you have any doubt, let me know. I am there for solution.